|
|
|
|
OPNET Technologies OPNET is a registered
|
University:
National Autonomous University of Mexico Department: Telecommunications Engineering
Research with OPNET MODELER
We are using Opnet Modeler to develop a simulation model for Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) Networks based on the IEEE 802.16 standards. With this model we expect to carry out a general evaluation of IEEE 802.16 networks. This kind of analysis is very important because it permits to obtain the shortcomings and reaches of the networks. We are also providing some enhancements to the IEEE 802.16e and IEEE 802.16-2004 standards in order to increase the systems performance.
Performance Analysis of Hand-off procedures for IEEE 802.16e
This project focuses on the development of hand-off (HO) mechanisms to provide mobility to subscriber stations based on the IEEE 802.16e protocol, supporting quality of service to offer services such as: VoIP (Voice over IP), Multimedia services or any required by the users. A simulation model based on OPNET MODELER v11 is being developed to evaluate the performance of the proposed HO mechanism.
Performance Analysis of Scheduling Algorithms for IEEE 802.16-2004
This research presents a performance analysis of different scheduling techniques for the provision of QoS in Fixed Broadband Wireless Access Networks (BWA). The performance is based on the MAC protocol proposed for the IEEE 802.16-2004 standard. It focuses on the uplink channel, which is the limiting factor of BWA networks and is critical in the delivery of services to individual users on demand. Although the IEEE 802.16 standard had proposed several QoS techniques for various types of applications, it doesn´t suggest how to schedule traffic to fulfill timing critical services such as compresed/uncompresed voice, audio and video streams. We are implementing a novel scheduling algorithm that combines Round Robin, Early Deadline First and Prioritization, to perfect match VBR-like and CBR-like traffic for IEEE 802.16 based networks. Simulation results will show that real-time services can be supported with very low access delays even during congestion periods.
Publications with OPNET MODELER
CONFERENCE Análisis de Técnicas de Modulación Adaptiva en Redes Inalámbricas de Banda Ancha (IEEE 802.16) (PDF) La tecnología de acceso inalámbrico revolucionará la forma de comunicación que hoy en día se utiliza para la transmisión de servicios digitales. Tendencias a nivel mundial indican que los sistemas de banda ancha de acceso inalámbrico (BWA), surgirán como una nueva tecnología complementaria para brindar servicios y aplicaciones, que en su conjunto puedan utilizar canales de subida o bajada por arriba de lo 20 Mbps. Esta nueva tecnología BWA, de 4ta generación, será muy superior a la tecnología utilizada para proveer servicios de voz, video y datos, que en la actualidad son ofrecidos por compañías de telefonía celular de la 2da. y 3ra. generación. Para poder lograr altas tasas de transmisión de datos, por arriba de los 20Mbps es indispensable optimizar el uso de los canales inalámbricos. Esta optimización se logra al utilizar diferentes técnicas de modulación que permitan a los usuarios subscriptores que se encuentren cerca de la estación base (BS-Base Station) enviar información a tasas más altas que los usuarios que se encuentren lejos de la BS. En este artículo se presenta un análisis del comportamiento dinámico de una técnica de modulación adaptiva que combina QPSK, 16-QAM y 64-QAM, en regiones de reservación y de contención, para poder lograr una mejor utilización en los canales de subida “uplink” (UL) basado en el protocolo IEEE 802.16. V. Rangel, X. Lopez, C. Mora, J. Gómez, “Análisis de técnicas de modulación adaptiva en redes inalámbricas de banda ancha”, III Simposio La Investigación y Desarrollo en la Facultad de Ingeniería-UNAM, Noviembre 2006. Comparative Analysis of Wireless Broadband Mesh and Multihop Networks (PDF) This paper provides a comparative analysis of wireless broadband mesh and multi-hop networks. This analysis focuses on synchronization and centralized and distributed scheduling in wireless broadband mesh networks. In addition, it also describes the additional addressing and connection definition that applies to multihop relay systems. The comparative analysis is made on the basis of conceptual flow diagrams. 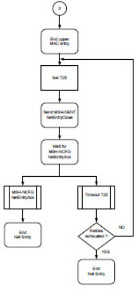 R. Aquino-Santos, V. Rangel-Licea, A. González-Potes, L.A. Villaseñor-González, M. García-Ruiz, A. Edwards-Block, S. Sandoval-Carrillo, “Comparative Analysis of Wireless Broadband Mesh and Multi-hop Networks”, Proceedings of the Electronics, Robotics and Automotive Mechanics Conference (CERMA), Cuernavaca, Morelos, México, September 2008, ISBN:978-0-7695-3320-9, pp. 157-162. Performance Evaluation of Five New Adaptive Contention Slot Allocators for IEEE 802.16 Based Systems (PDF) A reservation based Medium Access Control (MAC) protocol has been adopted by the IEEE 802.16 standard as the basic protocol for data communication within the upstream channel. In this paper, we propose the following five new Contention Slot Allocators (CSA) for the IEEE 802.16 MAC protocol: Forced-CSA, Variable-CSA, Multicast-CSA, Collision Free-CSA and CDMA-CSA. The new techniques dynamically fit the number of contention slots needed to solve collisions according to the current traffic load, considerably improving overall system performance. The CSAs introduced in this paper indicate that the mean access delay could be reduced up to 75% compared with the currently adopted method by the IEEE 802.16 MAC Protocol, called Simple-CSA. A performance evaluation of our five CSA schemes is presented and compared with previous CSA schemes, Simple-CSA and IEEE 802.14-CSA. Obtained results turned out to be closer to the maximum estimated throughput than currently used methods. 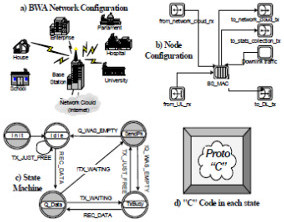 V. Rangel, M. Perez, J. Gomez, M. Lopez-Guerrero, R. Aquino, "Performance Evaluation of Five New Adaptive Contention Slot Allocators for IEEE 802.16 Based Systems", Proceedings of the IEEE Int. Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications, IEEE WiMob 2008, Abiñon, France, October 08, ISSN: 1930-529X, ISBN: 978-1-4244-2324-8, pp. 316-321. Performance Optimization of the Initialization Process of IEEE 802.16 Mesh Networks (PDF) The IEEE 802.16-2004 standard defines a medium access control (MAC) layer for a mesh network topology. In these networks, wide scale power outages can cause serious disruptions to digital services when centralized scheduling is used. This results in very long service recovery times for all mesh nodes. In this paper we propose a new recovery scheme and study the performance of the initialization process due to service disruption of IEEE 802.16-2004 mesh networks. We implemented an OPNET simulation model of the scheme. Results show that the recovery times obtained with the proposed scheme can be reduced by up to 98% compared with the default mechanism. 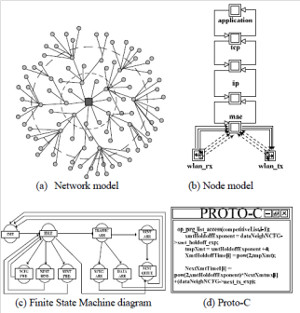 V.Rangel, Y. Macedo, J. Gomez, M.Lopez-Guerrero, R.Aquino, A.Edwards, "Performance optimization of the initialization process of IEEE 802.16 mesh networks". Electrical and Computer Engineering (CCECE) Sch. de Inglaterra., Nat. Univ. Autónoma. de México, Ciudad de México, 2010, 23rd, Canadian Conference, May 2-5, 2010, ISBN: 978-1-4244-5376-4,pp.1-5. Contention Resolution Algorithms for CATV Networks Based on the DVB/DAVIC Protocol (PDF) In a bi-directional Community Antenna Television (CATV) Network the use of a Contention Resolutions Algorithm (CRA) is essential in order to allocate the bandwidth of the multiaccess medium in the upstream direction between the active stations. Two of the CRAs known as exponential backoff algorithm and splitting tree algorithm, have recently been adopted by the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB)/Digital Audio-Visual Council (DAVIC) Cable Television Protocol. In this paper we present a performance analysis and a comparison of both algorithms in terms of mean access delay and system throughput for different traffic source scenarios (i.e. Internet traffic, Voice over IP, and mixed traffic). The analysis focuses on changes in performance when selecting different backoff bounds for the exponential backoff algorithm and different values for the Entry-Spreading factor of the splitting tree algorithm. The results presented here show that an increase over 10% in system performance can be obtained by selecting the splitting tree algorithm for different traffic sources. 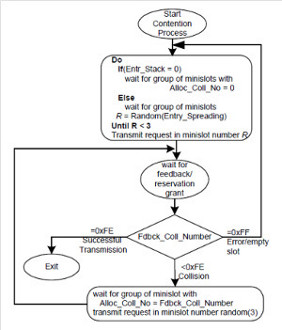 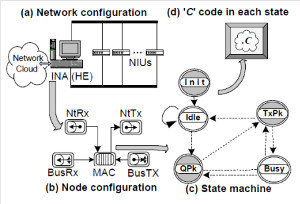 V. Rangel, R. Edwards, and K. Schunke, “Contention Resolution Algorithms for CATV Networks Based on the DVB/DAVIC Cable Modem Protocol Specification (ETS EN 200 800)”, Proc. of the International Broadcasting Conference (IBC), Amsterdam, vol. I, pp. 193-202, September 2001. A Comparison of the DVB/DAVIC, DOCSIS and IEEE 802.14 Cable Modem Specifications (PDF) Community Antenna Television (CATV) standardizing organizations are working on the provision of a unified standard that will allow the development of interoperable hardware and drive down the cost of implementation. The Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB)/ Digital Audio-Video Council (DAVIC), the Multimedia Cable Network systems (MCNS)/Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS), and the IEEE 802.14 protocols are focused on the current cable modems. These protocols share a common goal to provide interface specifications for the support of the same services (e.g. telephony, internet access, remote access, videoconferencing, etc.). The aim of this paper is to provide a comparative analysis of reference architectures, Media Access Control (MAC) and physical layer characteristics; as well as a comparative performance evaluation in terms of volumetric data and efficiency among these cable modem protocols. 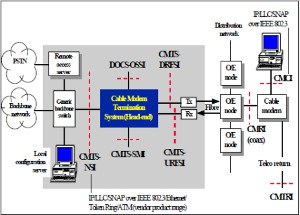 V. Rangel , C. Smythe, P. Tzerefos, S. Cvetkovic and S. Landeros, “A comparison of the DVB/DAVIC, DOCSIS and IEEE 802.14 Cable Modem Specifications”, Proc. of the International Conference on Telecommunications (ICT 2000), ISBN 968-36-7763-0, vol. 1, pp. 503-508, Acapulco, Mexico, May 2000. Performance Analysis of QoS Scheduling in Broadband IEEE 802.16 Based Networks (PDF) This paper presents the design and performance analysis of a scheduling technique for the provision of QoS over Broadband Wireless Access Networks (BWA). The proposed scheduling algorithm is based on the MAC protocol of the IEEE 802.16 standard and focuses on the uplink channel, which is the limiting factor of BWA networks and is critical in the delivery of services to individual users. Although the IEEE 802.16 standard had proposed several QoS service classes for various types of applications, they do not suggest how to schedule traffic to fulfill timing critical services such as compresed/uncompressed voice, audio and video streams. We have derived a mechanism called EBSA that combines several scheduling algorithms to closely match VBR like and CBR-like traffic over the IEEE 802.16 air interface. Simulation results show that EBSA provides real-time services with very low access delays even during congestion periods 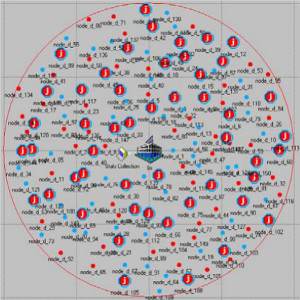 V. Rangel, J. Gómez y J. Ortiz, “Performance Analysis of QoS Scheduling in Broadband IEEE 802.16 Based Networks”, Proc. of OPNETWORK Technology Conference, vol 1566, Washington, USA, August 2006. Performance Analysis of a Reliable Handoff Procedure for IEEE 802.16e based networks (PDF) IEEE 802.16 is a protocol for fixed broadband wireless access that is currently trying to add mobility among mobile users in the standard. However, mobility adds some technical barriers that should be solved first, this is the case of HO “handoff” (change of connection between two base stations “BS” by a mobile user). In this paper, the problem of HO in IEEE 802.16 is approached trying to maintain the quality of service (QoS) of mobile users. A mechanism for changing connection during HO is presented. A simulation model based on OPNET MODELER v11 was developed to evaluate the performance of the proposed HO mechanism. Finally, this paper demonstrates that it is possible to implement a seamless HO mechanism over IEEE 802.16 even for users with demanding applications such as voice over IP. 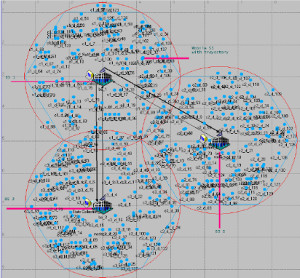 V. Rangel, J. Gómez y E. Cota, “Performance Analysis of a Reliable Handoff Procedure for IEEE 802.16 Based Networks”, Proc. of OPNETWORK Technology Conference, 2006, vol. 1566, Washington, USA, August 2006. Performance Analysis of Best Effort Support in Broadband IEEE 802.16 Networks (PDF) This paper presents a performance analysis of best effort support over the MAC protocol proposed in the IEEE 802.16 standard. We focus on the uplink channel since it is the critical element for efficient delivery of services on demand to individual users (i.e., Best Effort service). We describe a modeling approach and derive the resulting analytical model. Such a model allows us to efficiently compute network throughput. We test this model by means of computer simulations which are also reported in this paper. Simulation results and theoretical computations showed a close agreement, thus validating the model. 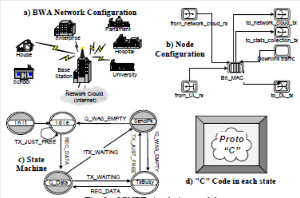 V. Rangel, J. Gomez, J. Chapa, M. Lopez-Guerrero, Raul Aquino. "Performance Analysis of Best Effort Support in Broadband IEEE 802.16 Networks". IEEE CCECE 2009, Delta St. John's, St. John's. Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada, May 3-6, 2009.
JOURNAL QoS Management for Broadband IEEE 802.16 based Networks in FDD Mode (PDF) Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) has become the best way to meet residential and small business demand for high speed Internet access and multimedia services. As an emerging technology for broadband access, it provides the following advantages over its wired competitors: 1) rapid deployment and ease to implement; a BWA network can be installed rapidly without extensive underground cable infrastructure as is the case of Cable or DSL networks, 2) high scalability; carriers can expand the BWA network as subscriber demand for bandwidth grows by adding channels, or cells, 3) lower maintenance and upgrade costs and 4) higher data rates. However, the wide-scale adoption of BWA systems will be determined by its ability to overcome cost and performance barriers. If BWA can meet these challenges it could easily be the next revolution in wireless networks systems such as WLANs. 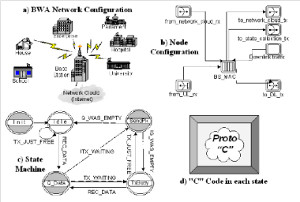 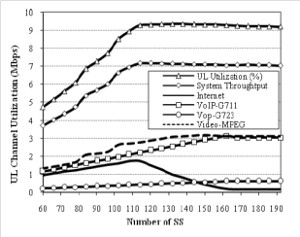 V. Rangel, Y. Macedo, L. Ortiz, J. Gómez. "QoS Management for Broadband IEEE 802.16 Based Networks in FDD Mode". Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering (Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika), Vol. 98, No.2, ISSN 1392-1215, February 2010, Indexed in SCI-E. Performance Evaluation of Adaptive Contention Slot Allocators for CATV Networks based on the European Cable Communications Protocol (PDF) Community Antenna Television (CATV) networks were originally designed for one-way analogue TV broadcasting (from the headend to residential areas). They are now being upgraded to provide a return path, referred as upstream channel, (from the home to the headend). New challenges arise in using the upstream channel due to the reduced bandwidth and the high levels of noise. The efficiency of the CATV MAC protocol depends highly on the bandwidth assigned to the contention access region. A high number of contention slots assigned to this region, reduces the bandwidth for data transmission. On the other hand, a small number of contention slots, results in an increased number of collisions with high traffic loads and degradation in system performance. In this paper, three adaptive contention slots allocators (CSA) are presented for the European Cable Communications Protocol: Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB)/ Digital Audio-Visual Council (DAVIC). These techniques dynamically adjust the number of contention slots needed to resolve collisions according to the traffic load, considerably improving overall system performance. 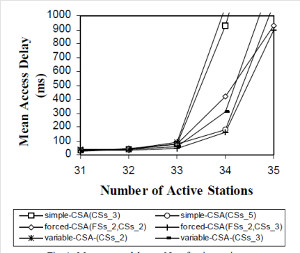 V. Rangel and R. Edwards. Performance Evaluation of Adaptive Contention Slot Allocators for CATV Networks based on the European Cable Communications Protocol" , Journal of Cable Telecommunication Engineering (CTE), No. 24, September 2002. Performance Analysis of QoS Over CATV Networks Based on the European Cable Modem Protocol (DVB/DAVIC) for the Support of Delay Sensitive Applications (PDF) This paper presents an overview of some key QoS features that will enable the DVB/DAVIC protocol with a superior performance and efficiency at the Media Access Control (MAC) layer for the support of delay-sensitive applications. We show the deficiencies of the basic reservation request mechanism provided by the DVB/DAVIC MAC protocol and present a performance optimisation via simulation results in terms of mean packet access delay and system throughput. Initial results show that the number of delay sensitive streams supported can be increased considerably by considering QoS features. 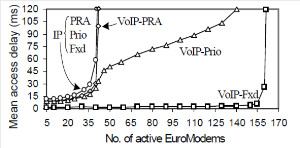 V. Rangel and R. Edwards, Performance Analysis of QoS over CATV Networks Based on the DVB/DAVIC Protocol”, Journal of Cable Telecommunication Engineering (CTE), vol. 25, March 2003. Design of handoff procedures for broadband wireless access IEEE 802.16 based networks (PDF) IEEE 802.16 is a protocol for fixed broadband wireless access that is currently trying to add mobility among mobile users in the standard. However, mobility adds some technical barriers that should be solved first, this is the case of HO “handoff” (change of connection between two base stations “BS” by a mobile user). In this paper, the problem of HO in IEEE 802.16 is approached trying to maintain the quality of service (QoS) of mobile users. A mechanism for changing connection during HO is presented. A simulation model based on OPNET MODELER1 was developed to evaluate the performance of the proposed HO mechanism. Finally, this paper demonstrates that it is possible to implement a seamless HO mechanism over IEEE 802.16 even for users with demanding applications such as voice over IP. 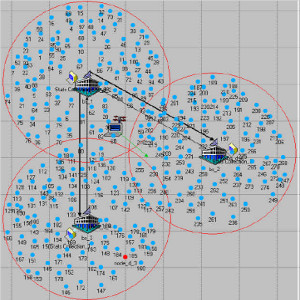 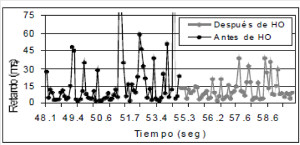 V. Rangel, E. Cota y J. Gómez, Design of handoff procedures for broadband wireless access IEEE 802.16 based networks, INGENIERIA INVESTIGACION Y TECNOLOGIA, Facultad de Ingeniería UNAM, Vol. IX, No. 1, Enero-Marzo 2008, ISSN 1405-7743 Enhanced Network Control for the Entry Process of IEEE 802.16 Mesh Networks (PDF) The IEEE 802.16-2004 standard [1] supports the following two operating modes of the Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer: a) point to multipoint (PMP) mode, where traffic occurs only between the Base Station (BS) and Subscriber Stations (SSs), and b) mesh mode, where traffic can be routed through other SSs and can occur directly between SSs. In mesh mode, system throughput can be increased by using multiple-hop paths [2-3]. Thus, wireless mesh networks (WMNs) can be used to extend cell ranges, cover shadowed areas and enhance system throughput. 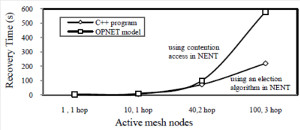 Y.Macedo, V. Rangel, J. Gómez, M. Lopez-Guerrero, R. Aquino, “Enhanced Network Control for the Entry Process of IEEE 802.16 Mesh Networks”.To be published in Journal of Electronics and Electrical Engineering. publication in February 2012, Vol.118, no.02.ISSN 1392 – 1215. Contention Resolution Algorithms for CATV Networks Based on the DVB/DAVIC Protocol (PDF) In a bi-directional Community Antenna Television (CATV) Network the use of a Contention Resolutions Algorithm (CRA) is essential in order to allocate the bandwidth of the multiaccess medium in the upstream direction between the active stations. Two of the CRAs known as exponential backoff algorithm and splitting tree algorithm, have recently been adopted by the Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB)/Digital Audio-Visual Council (DAVIC) Cable Television Protocol. In this paper we present a performance analysis and a comparison of both algorithms in terms of mean access delay and system throughput for different traffic source scenarios (i.e. Internet traffic, Voice over IP, and mixed traffic). The analysis focuses on changes in performance when selecting different backoff bounds for the exponential backoff algorithm and different values for the Entry-Spreading factor of the splitting tree algorithm. The results presented here show that an increase over 10% in system performance can be obtained by selecting the splitting tree algorithm for different traffic sources. 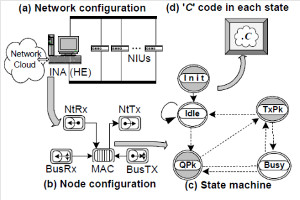 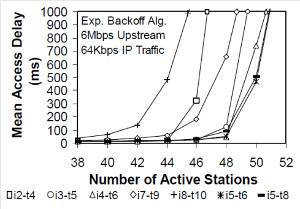 V. Rangel, R. Edwards, and K. Schunke, Contention Resolution Algorithms for CATV Networks Based on the DVB/DAVIC Cable Modem Protocol Specification (ETS EN 200 800), Journal of Cable Telecommunication Engineering (CTE), December 2002. Inter-Vehicular Communications Using Wireless Ad-Hoc Networks (PDF) This paper proposes a new routing algorithm to facilitate communication in highly mobile wireless ad-hoc networks for motorway environments with no physical infrastructure which undergo frequent topological changes. This new reactive routing algorithm for inter-vehicular communication is based on location information in which the source node ascertains the position of its communication partner before it initiates communication. The advantage of this algorithm is that it does not require global knowledge to send information between transmitter-receiver pairs. Instead, this algorithm requires knowledge of the relative positions of its neighbor nodes and the position of the destination. This paper discusses simulations of 250 vehicles driving on a six-lane circular highway using Location Routing Algorithm with Cluster-Based Flooding (LORA-CBF). Highway vehicular mobility is simulated by a microscopic traffic model, developed in OPNET, to evaluate the performance of the LORA-CBF and Greedy Perimeter Stateless Routing (GPSR) algorithms in terms of Route Discovery Time (RDT), End-to-End Delay (EED), Routing Overhead (RO), Routing Load (RL) and Delivery Ratio (DR). 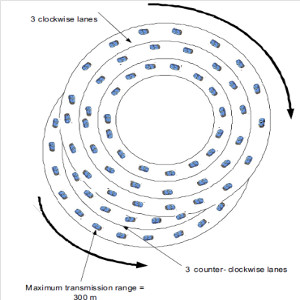 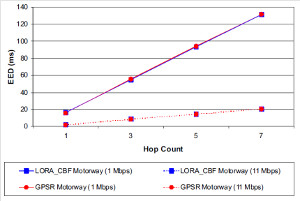 R. A. Santos, V. Rangel, A. Edwards, Inter-Vehicular Communications using Wireless Ad Hoc Networks”, INGENIERIA INVESTIGACION Y TECNOLOGIA, Facultad de Ingeniería UNAM, Vol. IX, No. 4, Octubre-Diciembre 2008, ISSN 1405-7743. Performance evaluation of VoIP traffic over the IEEE 802.16e protocol with different modulations and codings (PDF) Supporting as many Voice over IP (VoIP) users as possible in a BWA network using limited radio resources is a very important issue. However, performance of VoIP services is affected by several issues defined in the IEEE 802.16e protocol. In this paper we used a theoretical model and an algorithm to evaluate the performance of some of the most important VoIP codecs. Simulation results validate the theoretical model to achieve the maximum number of VoIP streams for different configurations of the IEEE 802.16e system 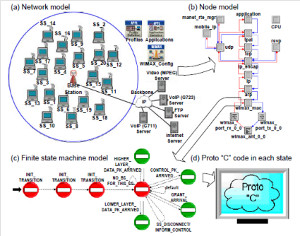 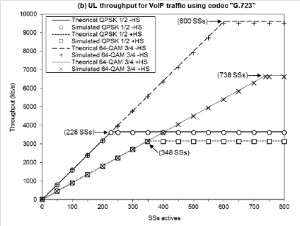 L. Ortiz, V. Rangel, J. Gomez, R. Aquino, M. Lopez-Guerrero, “Performance evaluation of VoIP traffic over the IEEE 802.16e protocol with different modulations and codings. PRZEGL?D ELEKTROTECHNICZNY (Electrical Review), Vol 2013, February 2013, ISSN 0033-2097, Indexed in JCRY. Wireless Propagation Characteristics for Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks in Motorway Environments (PDF) This paper presents the measurements and analytical results made over important characteristics of wireless propagation for vehicular ad-hoc networks in motorway environments, including Doppler Effect, Free Space Signal propagation, path loss and system operating margin. In this work, we employ IEEE 802.11b wireless cards for inter-vehicular communication to analyze large and small-scale propagation models. According to large-scale models, the maximum distance between the transmitter and receiver vehicle is 446m using 5dBi omni-directional antennas. Additionally, the feasible System Operating Margin (SOM) of 446m is over 13 dB, which is over the minimum margin recommended. Our results show that the Doppler Effect does not affect transmission between communication partners at high speeds in small-scale models. Finally, we realize an experiment to validate the former results in the worst case scenario, when the transmitter and receiver vehicle are traveling in opposing directions on a straightaway. Results show that at least 8 packets can be relayed when the transmitter and receiver antennas are mounted on automobile dashboards. R. A. Santos, V. Rangel, L. Villaseñor, A. Edwards, Wireless Propagation Characteristics for Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks in Motorway Environments .Accepted for publication in January 2009, INGENIERIA INVESTIGACION Y TECNOLOGIA, Facultad de Ingeniería UNAM, ISSN 1405-7743, 2009. CHAPTER BOOK'S Analyzing IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.16e Technologies for Single-hop Inter-Vehicle Communications. (PDF) This chapter analyzes two prominent technologies, IEEE 802.11g (WiFi) and IEEE 802.16e (WiMAX), for single-hop inter-vehicular communications. We begin our analysis by comparing the physical and MAC layers of both standards. Following this, we simulate two scenarios, one with IEEE 802.11g and the other with IEEE 802.16e, in a single-hop intervehicular communication network (SIVC). In both scenarios, the Location-Based Routing Algorithm with Cluster-Based Flooding (LORA-CBF) was employed to create a hierarchical vehicular organization that acts as a cluster-head with its corresponding member nodes. The simulation scenarios consist of five different node sizes of 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 vehicles, respectively. We propose a novel simulation model that is suitable for mesh topologies in WiMAX networks and provide preliminary results in terms of delay, load and throughput for single-hop inter-vehicle communication. 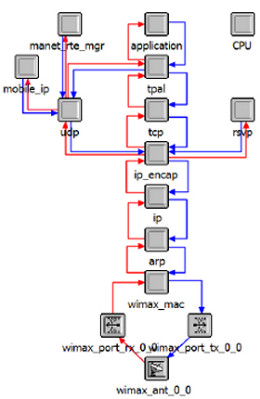 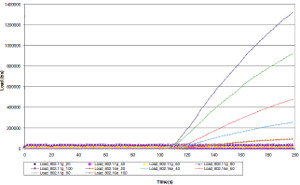 R. Aquino-Santos, V. Rangel-Licea, A. Méndez, Miguel A. García-Ruiz and A. Edwards-Block. Chapter Title: Analyzing IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.16e Technologies for Single-hop Inter-Vehicle Communications. Book Title: Advances in Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks: Developments and Challenges. IGI Global (in press), 2010, Editor: Mohamed Watfa. ISBN: 978-1-60566-338-8. Inter-vehicular Communications using Wireless Ad Hoc Networks. (PDF) This chapter proposes a new routing algorithm that allows communication in vehicular ad hoc networks. In vehicular ad hoc networks, the transmitter node cannot determine the immediate future position of the receiving node beforehand. Furthermore, rapid topological changes and limited bandwidth compound the difficulties nodes experience when attempting to exchange position information. The authors first validate our algorithm in a small-scale network with test bed results. Then, for large-scale networks, they compare our protocol with the models of two prominent reactive routing algorithms: Ad-Hoc On-Demand Distance Vector and Dynamic Source Routing on a multi-lane circular dual motorway, representative of motorway driving. Then the authors compare their algorithm with motorway vehicular mobility, location-based routing algorithm, on a multi-lane circular motorway. This chapter then provides motorway vehicular mobility results of a microscopic traffic model developed in OPNET, which the authors use to evaluate the performance of each protocol in terms of: Route Discovery Time, End to End Delay, Routing Overhead, Overhead, Routing Load, and Delivery Ratio.  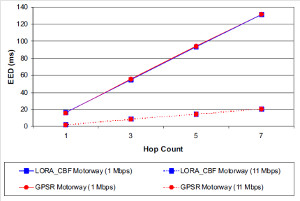 R. Aquino-Santos, V. Rangel-Licea, M. A. García-Ruiz, A. González-Potes, O. Álvarez-Cárdenas, A. Edwards-Block, M. G. Mayoral-Baldivia and S. Sandoval-Carrillo. Chapter title: Inter-vehicular Communications using Wireless Ad Hoc Networks. Book title: Automotive Informatics and Communicative Systems Principals in Vehicular Networks and data Exchange. IGI Global, April, 2009. ISBN: 978-1-60566-338-8.
Last updated: February 2013.
|